1. Physical Geography is the study of.......
a. the spatial relationships and interactions within and between major cities and their relationship to each other.
b. the spatial relationships and interactions within and between people and their relationship to Earth.
c. the spatial relationships and interactions within and between the major Earth systems and their relationship to humans.
d. the social, economic, and behavioral processes that differentiate places on Earth.
e. none of the above.
2. What are the four major systems of the larger Earth system?
3. A scientific model can be described as a set of rules that explain how reality works.
a. TRUE b. FALSE
4. Define scientific theory.
5. What are the basic hallmarks that make scientific theory valid?
6. What provides the underpinnings of physical science?
7. The conservation of mass is the idea that...
a. mass cannot be created, but can be used up whenever work is performed.
b. mass is neither created nor destroyed, but transformed from one state to another.
c. mass cannot be created, but can be destroyed.
d. inputs of mass into a system are always greater than outputs.
e. both a and c
8. Entropy is a measure of a systems ability to perform work.
a. TRUE b. FALSE
9. Which of the following is a form of energy?
a. chemical
b. radiant
c. kinetic
d. electrical
e. all of the above
10. What was Einstein's contribution to the 1st law of thermodynamics?
THE GEOGRAPHIC GRID
1. Your best friend told you about an amazing waterfall that is located off the beaten path and difficult to find.
The only locational information your friend gave you was the Latitude of the waterfall: 38 degrees North.
Can you find it? Explain your answer.
2. Which of the following lines of the geographic grid are orientated North to South?
a. Latitude Lines
b. 120º West
c. Meridians
d. 15º South
e. both b and c
3. Which of the following lines of the geographic grid are great circles?
a. equator c. all longitude lines e. both a and c
b. 23.5º N d. all lines in the geographic grid
4. All lines of latitude converge at the North and South poles.
a. TRUE b. FALSE
5. Parallels are orientated perpendicular to the axis of rotation.
a. TRUE b. FALSE
6. What is the name for a line on a map that connects points of equal value?
7. Using a topographic map, if you travel parallel to the contour lines without crossing them...
a. you will increase in elevation.
b. you will decrease in elevation.
c. your elevation will not change.
d. both a and b.
e. None of the Above.
8. Contour lines that are close together will indicate _____________ , compared to contour lines
that are spread further apart.
a. steep terrain c. flat terrain e. None of the Above
b. gentle terrain d. shorter distances
Questions 9-10 refer to the following diagram:
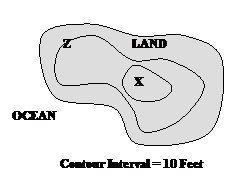
9. What is the elevation at point Z?
a. 0 feet
b. 5 feet
c. 10 feet
d. 20 feet
e. 30 feet
10. What is the elevation at point X?
a. 10 feet
b. 30 feet
c. 40 feet
d. >20 and <30
e. >30 and <40
EARTH SUN RELATIONSHIPS
1. What direction does the Earth rotate?
a. East to West c. West to East
b. North to South d. South to North
2. If you are in Phoenix, at any point in time it will always be earlier in the day at.....
a. New York
b. Chicago
c. Anchorage
d. Miami
e. both a and b
3. The angular velocity of the Earth's axial movement is.....
a. 15º Longitude/hr c. 90º Longitude/hr e. none of the above
b. 45º Longitude/hr d. 180º Longitude/hr
4. Our system of time is based on 24 standard time zones that are each 10º Longitude wide.
a. TRUE b. FALSE
5. The linear speed at the Earth's surface is constant and does not vary spatially.
a. TRUE b. FALSE
6. Describe the "crime of Galileo" and his discovery about the moon?
7. What are the 4 major characteristics of Earth revolution about the sun?
8. The solar declination....
a. is the position of the sun at noon.
b. is the line of latitude over which the sun is directly overhead on any given day.
c. is the line of longitude over which the sun is directly overhead on any given day.
d. is over San Diego on the June solstice.
e. is directly over the equator only once a year.
9. How many times a year is the sun directly overhead at the Tropic of Capricorn?
a. 0
b. 1
c. 2
d. 3
e. 4
10. The axis of Earth's rotation is orientated parallel to the plane of the ecliptic and varies 23 1/2º annually.
a. TRUE b. FALSE
INCOMING SOLAR RADIATION
1. One wave of longwave radiation has...
a. more intense energy than one wave of shortwave radiation.
b. less intense energy than one wave of shortwave radiation.
c. the same energy as one wave of shortwave radiation.
d. None of the above.
2. The Earth emits shorter wavelengths of light than the sun.
a. TRUE b. FALSE
3. The EMR spectrum classifies light into categories based on wavelength. This classification is often illustrated on...
a. an arithmetic axis c. a rotational axis
b. a logarithmic axis d. none of the above
4. The Stefan-Boltzmann law states that the total energy radiated by a blackbody is directly proportional to...
a. (T)1 c. (T)3
b. (T)2 d. (T)4
5. Wien's law relates the wavelength of energy emitted by an object to the object's temperature.
The longer the wavelength, the hotter the temperature.
a. TRUE b. FALSE
6. Explain why the intensity of solar radiation receipt on Earth is maximized in the Tropics annually.
7. The absorption of Longwave Radiation in the lower atmosphere is associated most closely with which of
the following greenhouse gases?
a. nitrogen c. carbon dioxide
b. oxygen d. argon
8. Briefly describe the difference in insolation receipt at the North Pole vs. the South Pole on the June Solstice.
9. The major factors influencing variation in insolation receipt on Earth are...
a. sun angle c. solar flares e. all of the above
b. daylength d. both a and b
10. Radio waves are a type of radiation, and have longer wavelengths.
a. TRUE b. FALSE
THE GLOBAL ENERGY BUDGET
1. A dark surface, such as asphalt, has a higher albedo than a lighter surface, such as snow.
a. TRUE b. FALSE
For questions 2-5, match each process to the left with the corresponding energy transformation listed to the right.
|
2. Warming of the Earth’s surface by sunshine receipt. 3. Cloud formation by condensation 4. Reflection 5. Longwave emission by Earth’s surface |
A. No transformation Involved B. Latent Heat to Sensible Heat C. Sensible Heat to Latent Heat D. Radiant Energy to Sensible Heat E. Sensible Heat to Radiant Energy |
6. By what process does the Earth’s surface warm the lower atmosphere (troposphere)?
a. conductive and convective transport of sensible heat
b. longwave radiant energy emission
c. latent heat transport associated with the convection and subsequent condensation of water vapor
d. all of the above
7. Which of the following gases is most abundant in the Earth's atmosphere?
a. Oxygen c. Nitrogen e. None of the Above
b. Carbon Dioxide d. Water Vapor
8. Define sensible heat and latent heat. Give an example of a phase change that would convert sensible
heat energy to latent heat energy.
9. Global ocean circulation is partly responsible for distributing energy from the tropics towards the poles.
a. TRUE b. FALSE
10. Change, or variation, in the Sun Angle…..
a. causes variation in insolation receipt.
b. occurs diurnally and seasonally at any location.
c. for a given day will vary with a change in latitude.
d. all of the above
END OF REVIEW QUESTIONS FOR EXAM#1
AIR TEMPERATURE
1. Which of the following is true regarding the Kelvin scale of temperature?
a. Water freezes at 0K c. no negative numbers
b. Water boils at 273.15K d. absolute zero is not represented in the Kelvin scale
2. Water molecules are not moving when in a frozen state.
a. TRUE b. FALSE
3. Describe the difference between heat and temperature.
4. Convert 74ºF to K.
a. 23.3 K c. 296.5K e. None of the above
b. 379.2 K d. 106 K
5. In the Troposphere, an increase in elevation (holding all else constant) will lead to....
a. an increase in temperature.
b. a decrease in temperature.
c. no change in temperature.
d. at first, an increase in temperature, then a decrease.
e. none of the above.
6. The energy that heats the majority of the troposphere is coming directly from the sun as radiant energy. As particles of gas
in the atmosphere absorb most of the solar radiation, the atmosphere is warmed.
a. TRUE b. FALSE
7. The majority of weather processes and phenomena occur in which of the following layers of the atmosphere?
a. Stratosphere c. Thermosphere e. none of the above
b. Mesosphere d. Troposphere
8. The principle of continentality states that....
a. inland sites will have greater annual and diurnal ranges in temperature than coastal sites.
b. coastal sites will have greater annual and diurnal ranges in temperature than inland sites.
c. inland sites will have the same annual and diurnal ranges in temperature as coastal sites at the same latitude.
d. inland sites will have the same diurnal, but greater annual ranges in temperature than coastal sites.
e. None of the Above
9. Los Angeles and Phoenix are roughly on the same line of latitude. Explain the stark difference in annual and diurnal
temperature ranges.
10. Name the four major factors that influence variations in air temperature on the Earth's surface.
ATMOSPHERIC WINDS
1. In the Troposphere, with an increase in elevation the atmospheric pressure will....
a. increase at a constant rate. c. increase at a non-constant rate. e. none of the above
b. decrease at a constant rate. d. decrease at a non-constant rate.
2. On an isobar map, the pressure gradient is greater when....
a. isobars are parallel c. isobars are closer together e. none of the above
b. contours are closer together d. isobars are further apart
3. A surface isobar map can be used to determine relative differences in surface wind speed between locations.
a. TRUE b. FALSE
4. Which of the following influence surface winds?
a. The pressure gradient force c. Surface friction
b. The coriolis force d. all of the above
5. Why do winds in the tropopause flow parallel to isobars? What is the name for these winds?
6. Anticyclones are associated with all of the following EXCEPT....
a. high pressure c. rising air e. none of the above (all are associated)
b. convergence aloft d. clockwise rotation (N. Hemisphere)
7. The coriolis force is....
a. strongest at the equator c. stronger over land than ocean e. both a and c
b. strongest at the poles d. the same anywhere on Earth
Questions 8 - 10 refer to the following isobar map:
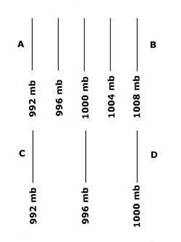
8. Assuming no coriolis effect or surface friction, air will move faster....
a. From A to B. c. From C to D. e. none of the above
b. From D to C. d. From B to A.
9. The pressure gradient force is....
a. weakest from D to C. c. absent in both scenarios.
b. weakest from B to A. d. the same in both scenarios.
10. Relatively speaking, high pressure is found at….
a. A and B c. B and D e. None of the above
b. C and D d. A and C
GLOBAL CIRCULATION
For questions 1-6, match each component of the Global Wind and Pressure System on the left
with the most appropriate location on the right:
|
1. Northeast Trade Winds 2. Subtropical High 3. Subpolar Low 4. Intertropical Convergence Zone 5. Polar Easterlies 6. Westerlies |
a. 60º N b. 0-30º N c. 30º N d. 60-90º N e. 30-60º N ab. 0º |
7. Which of the following are thermally-induced global pressure belts?
a. The Doldrums c. Low Pressure Belt at 0º Latitude e. All of the Above
b. The Equatorial Trough d. The Polar Anticyclone
8. A Northeast wind blows in what direction?
a. From the Northeast to the Southwest c. From the Southeast to the Northeast e. None of the Above
b. From the Southwest to the Northeast d. From the Northeast to the Northwest
9. On average, a monsoon occurs at about the same time every year.
a. TRUE b. FALSE
10. Briefly describe the seasonal pattern of rainfall associated with the Asiatic Monsoon.
MOISTURE AND CLOUD FORMATION
1. Water vapor in the atmosphere is visible as clouds and fog.
a. TRUE b. FALSE
2. An air mass has a dewpoint temperature of 58ºF. The current temperature of the air mass is 58ºF. Which of the
following statements are FALSE regarding the air mass?
a. The air mass is saturated
b. Condensation is occurring
c. The relative humidity is 100%
d. The specific humidity is decreasing
e. None of the above
3. Which of the following statements are TRUE regarding a rising parcel of air in the atmosphere?
a. The capacity of the air to hold water vapor will increase.
b. The relative humidity of the air mass will decrease.
c. The air molecules will expand causing adiabatic warming.
d. The air will cool at the DALR as long as the relative humidity is less than 100%.
e. The specific humidity of the air mass will increase.
4. Why is the rate of cooling of a parcel of air slower at the WALR compared to the DALR?
[WALR = Wet Adiabatic Lapse Rate (also called WAR)]
[DALR = Dry Adiabatic Lapse Rate (also called DAR)]
5. A desert is more likely to be found on the leeward side of a mountain than the windward side of a mountain.
a. TRUE b. FALSE
6. Which of the following are lifting mechanisms responsible for cloud formation?
a. Orographic c. Convective e. All of the above
b. Frontal d. Convergent (cyclonic)
7. Explain the temperature and humidity transformations that would take place to a parcel of air moving from
San Diego East over the mountains and into the desert. The initial conditions of the air mass at San Diego include
an air temperature of 80 degrees Fahrenheit and a dewpoint temperature of 36 degrees fahrenheit.
San Diego = 0 ft
Mountains = 6000 ft
Desert = 0 ft
8. An adiabatic change in temperature is a result of....
a. expansion of air
b. water changing phase from liquid to gas
c. compression of air
d. water changing phase from gas to liquid
e. both a and c
9. How does atmospheric moisture contribute to the global redistribution of energy from the tropics toward the poles?
10. Santa Ana winds bring warm temperatures to San Diego as a result of Adiabatic processes.
a. TRUE b. FALSE
TRAVELING WEATHER SYSTEMS
1. The development of a tropical cyclone is primarily a result of which lifting mechanism.
a. Orographic c. Adiabatic e. None of the Above
b. Convection d. Frontal
Questions 2-4 refer to the following illustration:
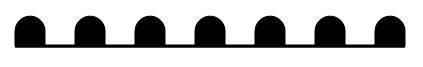
2. What type of front is represented above?
a. Warm c. Cold e. None of the above
b. Stationary d. Occluded
3. This type of front develops when....
a. cold air advances c. a cold front catches up to a warm front e. air is not moving.
b. warm air advances d. a warm front catches up to a cold front
4. What type of weather is typically associated with this type of front?
a. clear and dry conditions c. warm and rainy conditions e. None of the above
b. cold and rainy conditions d. warm and dry conditions
5. What type of air mass develops over the Gulf of Mexico?
a. mP c. mT e. None of the Above
b. cP d. cT
6. A cT air mass will typically have a higher specific humidity than a mT air mass.
a. TRUE b. FALSE
7. During hurricane season, it is common for hurricanes to develop.....
a. in the Gulf of Alaska. c. over cold ocean waters.
b. in the North Atlantic. d. over warm ocean waters.
8. A hurricane will become stronger as it moves over land.
a. TRUE b. FALSE
9. When advancing cold air comes in contact with warmer air, then....
a. the cold air will rise up over the warm air.
b. the warm air will rise up over the cold air.
c. the boundary between the two air masses will be a cold front.
d. the boundary between the two air masses will be a warm front.
e. both b and c.
10. How does the Jet Stream influence the occurrence of mid-latitude cyclonic storms?
END OF REVIEW QUESTIONS FOR EXAM#2
GLOBAL CLIMATE QUESTIONS
1. What is the difference between weather and climate?
a. Weather describes precipitation and wind while Climate describes global pressure and temperature.
b. Weather describes the long-term trend in atmospheric conditions while Climate describes the short-term trends.
c. Weather describes the short-term trends in atmospheric conditions while Climate describes the long-term trends.
d. Climate describes the effects of atmospheric conditions on land while Weather describes the actual atmosphere.
e. None of the above.
2. How would climate vary on a global scale if there were no continents?
3. The Koppen climate classification scheme uses what variables to describe differences in climate?
a. temperature c. precipitation e. both a and c
b. pressure d. wind
4. BS and BW climates can typically be found on the windward sides of mountains and in the 30 degree latitudes.
a. TRUE b. FALSE
Questions 5-7 refer to the following diagram:
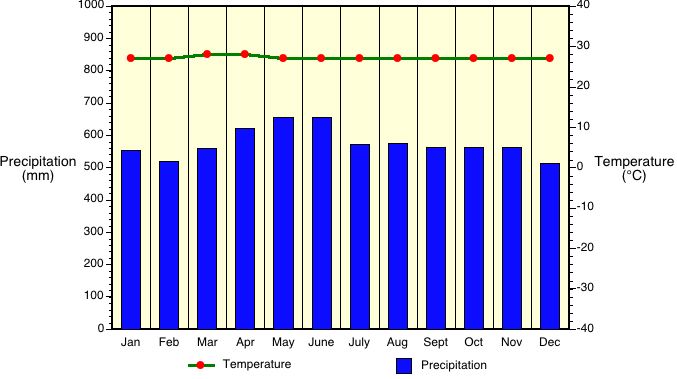
5. What climate is represented by the above graph?
a. Csa c. Af e. Aw
b. BWh d. As
6. Which statement is TRUE regarding the above climate?
a. Precipitation exceeds PET c. Outputs of moisture exceed inputs
b. PET exceeds Precipitation d. Temperature is greater than Precipitation
7. The above illustrated climate would most likely be found...
a. in Europe. c. in Brazil. e. None of these.
b. in Canada. d. in Texas.
8. Evapotranspiration is....
a. an input of moisture to an ecosystem. c. transpiration and evaporation. e. none of the above.
b. not influenced by plants. d. both b and c.
9. Photosynthesis is the process by which plants take in oxygen and produce carbon dioxide and water.
a. TRUE b. FALSE
10. In a BWh climate, which of the following plants would be native?
a. Conifer Tree c. Saguaro Cactus
b. Banana Tree d. Broad-leafed Deciduous Tree
THE BIOSPHERE QUESTIONS
1. Which of the following is NOT a component of the Biosphere?
a. Mid-latitude Forest c. Rainbow Trout e. None of the Above, all are components
b. Manzanita plant d. Insects
2. In a Cfa climate, which vegetation class would you expect to find?
a. Boreal Forest c. Desert e. Tropical Rainforest
b. Mid-latitude Forest d. Mid-latitude Grassland
3. The density of vegetation growth is greater for a Tropical Rainforest than a Mid-latitude forest.
a. TRUE b. FALSE
4. Vegetation growth in a Tropical Rainforest is....
a. one tiered. c. three tiered e. five tiered
b. two tiered. d. four tiered.
5. How have vegetation growing in deserts adapted to dry conditions?
a. smaller leaves c. more extensive roots e. all of the above
b. less leaves d. no leaves at all
6. As you travel poleward from the equator, how will the vegetation growth change in terms of height,
density of plants, density of growth, etc. ?
Questions 7-10 refer to the following 2 pictures


These pictures were taken in Colorado at approximately 40º N latitude.
7. In the top photo, what vegetation class is shown?
a. Mid-latitude Grassland c. Tundra e. None of the Above
b. Savanna d. Desert
8. In the lower photo, why are the trees only growing in one spot?
9. In the lower photo, the trees in the center of the photo are part of what vegetation class?
a. Mid-latitude Forest c. Tropical Deciduous Forest
b. Tropical Rainforest d. Conifer Forest
10. Are these two vegetation classes what you would expect to find at the 40º N latitudes?
If not, then why are they present here?
EARTH MATERIALS QUESTIONS
1. Weathering and Mass Wasting are processes that....
a. will form extrusive igneous rock c. result from endogenous energy
b. break down rock material into smaller fragments d. decrease entropy
2. If there were NO endogenic processes, the Earth's surface would be flat.
a. TRUE b. FALSE
3. Mass wasting processes, such as creep, landslide, rockfall, etc, are classified on
the basis of....
a. speed of movement c. amount of water present e. none of the above
b. type of rock material d. all of the above
4. Which of the following statements is TRUE about the density of matter on Earth?
a. Generally, the most dense matter is found at the Earth's surface.
b. Generally, density of matter is unorganized and varies at all layers within Earth.
c. Generally, matter is stratified into layers with the most dense material at the core.
d. Generally, matter is stratified into layers with the least dense material at the core.
e. None of the above
5. The internal Earth can be classified into 4 layers. What are those layers?
a. crust, liquid mantle, solid outer core, liquid inner core
b. crust, solid mantle, solid outer core, liquid inner core
c. crust, solid mantle, liquid outer core, solid inner core
d. crust, mesosphere, liquid outer core, solid inner core
e. crust, asthenosphere, solid outer core, liquid inner core
6. The asthenosphere is.....
a. a portion of the mantle that is hot and molds like tar.
b. a portion of the crust that is hot and molds like tar.
c. a portion of the outer core that is hot and liquid.
d. a portion of the outer core that is solid.
e. none of the above
7. Which of the following internal layers is the largest by volume?
a. crust c. outer core e. lithosphere
b. mantle d. inner core
8. The Earth's crust is thicker over oceans and thinner over land.
a. TRUE b. FALSE
9. Isostacy is the theory that the lithosphere floats on the asthenosphere and adjusts vertically.
a. TRUE b. FALSE
10. The three major rock types are....
a. igneous, intrusive, and extrusive.
b. igneous, sedimentary, and metamorphic.
c. intrusive, sedimentary, and extrusive.
d. igneous, sedimentary, and intrusive.
e. intrusive, metamorphic, and extrusive.
ROCK TYPES AND PLATE TECTONICS QUESTIONS
1. Granitic rock is also known as....
a. Igneous c. Plutonic e. None of the Above
b. Intrusive d. All of the Above
2. Which of the following is NOT a process within the rock cycle?
a. heat and pressure c. weathering and erosion e. None of the Above
b. cooling and melting d. compaction and cementation
3. Alfred Wegener is known for his proposed theory of.....
a. Plate Tectonics c. Continental Drift e. The Rock Cycle
b. Seafloor Spreading d. Orogenesis
4. The movement of lithospheric plates is driven directly by...
a. convection in the asthenosphere.
b. seafloor spreading.
c. earthquakes.
d. movement of magma in the Earth's core.
e. transform faults.
5. As you move away from a mid-ocean ridge, the oceanic crust will be younger.
a. TRUE b. FALSE
6. Converging plate boundaries are associated with....
a. spreading zones c. subduction zones e. tensional forces
b. orogenesis d. both b and c
7. Name two different types of faults and describe the differences between them,
the forces involved, and the direction of land movement on either side of the fault.
8. Both anticlines and synclines are a result of tension forces.
a. TRUE b. FALSE
Question #9 refers to the following picture...

9. What is the rock feature shown in this photograph?
a. Transform Fault c. Anticline e. both a and c
b. Syncline d. Recumbent Fold
10. Answer the following questions with regards to the San Andreas Fault.
The San Andreas Fault is very well known and significant. Why?
Where is it?
What 2 major lithospheric plates are separated by it?
What type of fault is it?
What major historical events have taken place as a result of it?
GRADATIONAL WORK QUESTIONS
1. Gradation is the process by which the physical landscape of the Earth's surface is flattened over time.
a. TRUE b. FALSE
2. Aggradation refers to....
a. the removal of Earth material from the landscape.
b. an erosional process where Earth material is weathered into smaller fragments.
c. the deposit of Earth materials on the landscape.
d. the process by which a glacier carves a valley into the landscape.
e. None of the Above.
3. River deltas, alluvial fans, and floodplain deposits are all examples of...
a. degradation. c. aggradation. e. None of the Above.
b. erosion. d. mass wasting.
4. Which of the following are gradational agents?
a. streams c. glaciers e. all of the above
b. ocean waves d. wind
5. As the erosional base level decreases in elevation, the potential erosional energy...
a. decreases c. does not change e. none of the above
b. increases d. dissipates and no more erosion occurs
6. Tectonic processes...
a. increase the erosional potential energy c. do not change the erosional potential energy
b. decrease the erosional potential energy d. promote maximum entropy on the landscape
7. Gradational processes work to promote....
a. maximum entropy c. minimum entropy e. none of the above
b. equilibrium d. both a and b
Question #8 refers to the following picture...
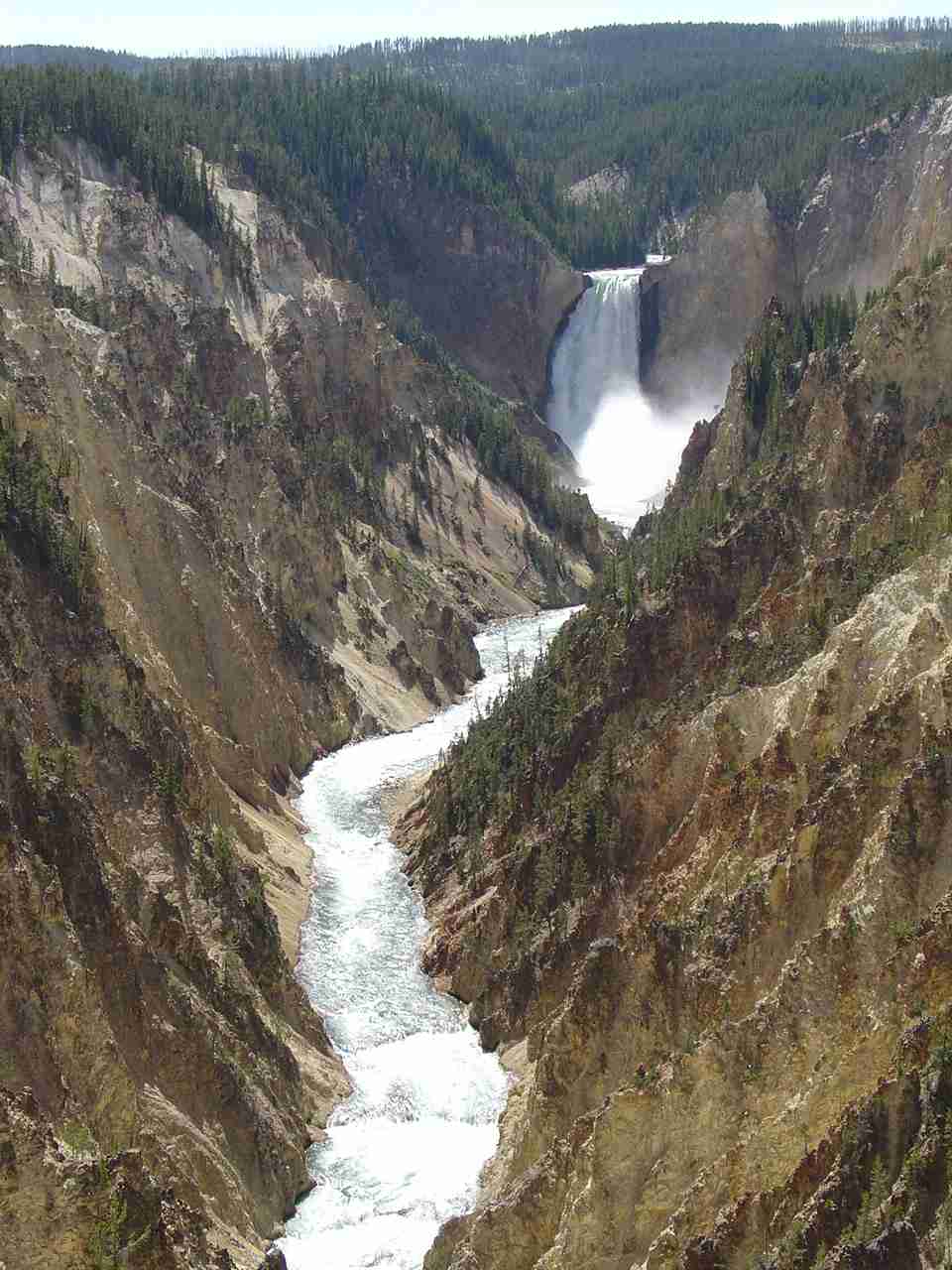

8. The above picture is an example of....
a. degradation c. erosion e. all of the above
b. transportation d. a gradational agent
9. Explain how an increase in elevation of the base level will change the potential erosional
energy of the stream, the entropy of the stream, and the gradational processes occurring within
the stream.
10. Referring to the equation representing stream discharge (Q = A x V), if the discharge decreases
and the area does not change, then the velocity must have increased.
a. TRUE b. FALSE
STREAM SYSTEM QUESTIONS
1. Near the headwaters of a stream, stream velocity is typically.....
a. less c. the same as in a floodplain
b. greater d. minimized
2. Streams with excess energy generally will have.....
a. more degradation than aggradation
b. more aggradation than degradation
c. the same general amount of aggradation and degradation at all points within the stream.
d. none of the above
3. The greater the stream power, the larger the material that can be eroded and transported down slope.
a. TRUE b. FALSE
4. Which of the following would potentially cause a reduction in stream energy?
a. An increase in sea level
b. The building of a dam on the stream
c. The depositing of material in a floodplain
d. Both a and c
e. All of the above
5. Floodplains are degradational features on the landscape.
a. TRUE b. FALSE
6. Within the floodplain, the stream will.....
a. erode material c. deposit material e. none of the above
b. transport material d. all of the above
7. Within a bend in a meandering stream, stream power is maximized....
a. at the outside edge of the bend in the stream
b. at the inside edge of the bend in the stream
c. in the center of the stream
d. none of the above, stream power is always minimized in a floodplain
8. Describe the processes responsible for the formation of an Oxbow lake in a floodplain.
9. Stream discharge is defined by the equation Q = A*V and carries units of cubic feet per second. If the
cross sectional area of a stream is increased, what will happen to the velocity?
a. It will increase c. It will stay constant
b. It will decrease d. None of the above
10. Explain how a stream system would be altered with the construction of a
dam in regards to the gradational work performed.
END OF REVIEW QUESTIONS FOR EXAM#3
EXAM #3 SHORT VERSION Q'S
EARTH MATERIALS QUESTIONS
1. Weathering and Mass Wasting are processes that....
a. will form extrusive igneous rock c. result from endogenous energy
b. break down rock material into smaller fragments d. decrease entropy
2. Which of the following statements is TRUE about the density of matter on Earth?
a. Generally, the most dense matter is found at the Earth's surface.
b. Generally, density of matter is unorganized and varies at all layers within Earth.
c. Generally, matter is stratified into layers with the most dense material at the core.
d. Generally, matter is stratified into layers with the least dense material at the core.
e. None of the above
3. The internal Earth can be classified into 4 layers. What are those layers?
a. crust, liquid mantle, solid outer core, liquid inner core
b. crust, solid mantle, solid outer core, liquid inner core
c. crust, solid mantle, liquid outer core, solid inner core
d. crust, mesosphere, liquid outer core, solid inner core
e. crust, asthenosphere, solid outer core, liquid inner core
4. The asthenosphere is.....
a. a portion of the mantle that is hot and molds like tar.
b. a portion of the crust that is hot and molds like tar.
c. a portion of the outer core that is hot and liquid.
d. a portion of the outer core that is solid.
e. none of the above
5. Which of the following internal layers is the largest by volume?
a. crust c. outer core e. lithosphere
b. mantle d. inner core
6. The Earth's crust is thicker over oceans and thinner over land.
a. TRUE b. FALSE
7. The three major rock types are....
a. igneous, intrusive, and extrusive.
b. igneous, sedimentary, and metamorphic.
c. intrusive, sedimentary, and extrusive.
d. igneous, sedimentary, and intrusive.
e. intrusive, metamorphic, and extrusive.
ROCK TYPES AND PLATE TECTONICS QUESTIONS
1. Granitic rock is also known as....
a. Igneous c. Plutonic e. None of the Above
b. Intrusive d. All of the Above
2. Which of the following is NOT a process within the rock cycle?
a. heat and pressure c. weathering and erosion e. None of the Above
b. cooling and melting d. compaction and cementation
3. Alfred Wegener is known for his proposed theory of.....
a. Plate Tectonics c. Continental Drift e. The Rock Cycle
b. Seafloor Spreading d. Orogenesis
4. The movement of lithospheric plates is driven directly by...
a. convection in the asthenosphere.
b. seafloor spreading.
c. earthquakes.
d. movement of magma in the Earth's core.
e. transform faults.
5. As you move away from a mid-ocean ridge, the oceanic crust will be younger.
a. TRUE b. FALSE
6. Converging plate boundaries are associated with....
a. spreading zones c. subduction zones e. tensional forces
b. orogenesis d. both b and c
7. Name two different types of faults and describe the differences between them,
the forces involved, and the direction of land movement on either side of the fault.
|
Points Earned on EXAM #1 |
Percent Grade |
Letter Grade |
|
More than 76 points |
96% or Higher |
A+ |
|
74 to 76 points |
92% to 95% |
A |
|
70 to 73 points |
88% to 91% |
A- |
|
68 to 69 points |
85% to 87% |
B+ |
|
65 to 67 points |
81% to 84% |
B |
|
62 to 64 points |
78% to 80% |
B- |
|
60 to 61 points |
75% to 77% |
C+ |
|
54 to 59 points |
67% to 74% |
C |
|
46 to 53 points |
58% to 66% |
D |
|
45 points or less |
57% or less |
F |
|
Points Earned in COURSE |
Percent Grade |
Letter Grade |
|
More than 324 points |
96% or Higher |
A+ |
|
312 to 324 points |
92% to 95% |
A |
|
298 to 311 points |
88% to 91% |
A- |
|
288 to 297 points |
85% to 87% |
B+ |
|
274 to 287 points |
81% to 84% |
B |
|
264 to 273 points |
78% to 80% |
B- |
|
254 to 263 points |
75% to 77% |
C+ |
|
227 to 253 points |
67% to 74% |
C |
|
196 to 226 points |
58% to 66% |
D |
|
195 points or less |
57% or less |
F |
FINAL GRADES NOW POSTED!
To my students.......
As the semester comes to an end, take a moment to reflect back on the things
you learned this semester. You should now have a better understanding of the
physical world around you. This knowledge will hopefully be useful throughout your life.
I am very proud of the dedication and hard work many of you have put forth. Your efforts
are not just working towards a degree. More importantly, your efforts are
helping you to learn how to learn better, and
to become a more educated, well-rounded individual.
Best wishes for you in all of your educational endeavors!
Judd Curran
PLEASE GIVE ME YOUR FEEDBACK
Click on the link to enter your comments
