1. Examples of how uniformitarianism is used to determine the age of the earth include: (1) Measuring sedimentation rates today and the thickness of sediments deposited in the past, to determine how much time would be required to deposit that much sediment. (2) Measuring radioactive decay rates today and the amount of radioactive material in a rock relative to stable daughter products, to determine how much time would be required to produce that parent to daughter ratio.
2. Absolute dating gives age in units of time. Relative dating compares the ages of events to tell the order in which they occurred.
3. COMPUTER ASSIGNMENT
4. The matching-up of rocks of similar ages in different regions is called correlation. Techniques of doing this include: (1) Demonstrate physical continuity. (2) Match-up similar rock types. (3) Find the same fossils in both regions.
5. Layer C is between 20 and 30my old. The absolute age of the folding in Australia is less than 30my. There are three unconformities evident in the European diagram. There is one unconformity evident in the Australian diagram.
6. a. C-14 b. K-40 c. U-238
7. The event that is actually being dated when K-40/Ar-40 dating is used is crystallization, or more specifically, the time when parent and daughter where separated.
8. The event that is actually being dated when radiocarbon (C-14) dating is used is death, or more precisely the time when the organism stopped extracting carbon from the environment.
9. 20,000 years
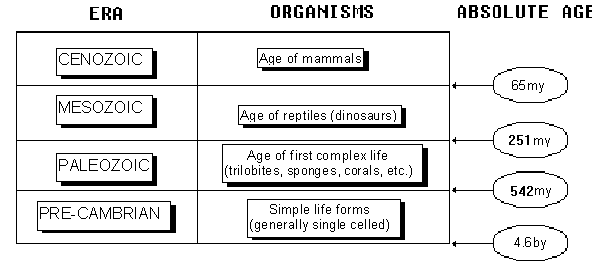
10.
8800 Grossmont College Drive
El Cajon, California 92020
619-644-7000
Accessibility
Social Media Accounts