1. The evidence for continental drift includes:
(1) The continents fit together into the super continent Pangaea. The fit improves when the continental shelves are included in the reconstruction.
(2) Fossils from the time of Pangaea are the same on different continents, but such matches are less common in fossils younger (or older) than Pangaea.
(3) Rocks and structures on different continents match-up when Pangaea is reconstructed.
(4) The distribution of ancient climates, as indicated by certain rocks, does not agree with the present distribution of climates unless the continents were in different places in the past.
Wagener's evidence was initially discounted because:
(1) The fit of the continents was poor because in most places Wegener had to use shorelines as the edge of the continents whereas the edge of the continental shelf is the true edge of the continent.
(2) It was believed that land bridges or island chains may have linked the continents in the past and provided ancient organisms with migratory routes between the continents.
(3) Wegener generally looked for evidence that fit his conclusions rather than conclusions that fit observations. Such methods can introduce bias into scientific conclusions by ignoring observations that do not support predetermined conclusions (e.g. Wegener did not address why some rocks and structures don't match when Pangaea was reconstructed.)
(4) Paleoclimate distributions could be explained by polar wandering instead of continental drift.
(5) Wagener did not present a plausible explanation as to the cause of continental drift.
The direction and inclination of magnetism in ancient rocks of the same age on different continents indicates that the magnetic North Pole was in several places at the same time. This is impossible, therefore you must move the continents to get the apparent pole positions to line-up.
2.
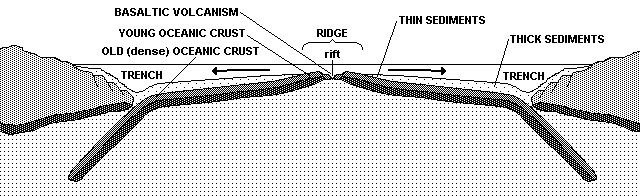
3. New oceanic crust is created along divergent plate boundaries. Divergence stretches and thins the lithosphere, thereby reducing the weight and pressure that the lithosphere exerts on the underlying asthenosphere. The drop in pressure causes partial melting in the asthenosphere so the resulting magmas will contain a slightly higher silica concentration than the asthenosphere and therefore be basaltic. This magma rises upward into the gap between the diverging plates, where it cools and solidifies into basalt. The process repeats as the plates diverge such that new basalt (oceanic crust) is continually added onto the trailing edges of both diverging plates.
Oceanic crust becomes older, colder and more dense as it moves away from the ridge. Eventually it and the uppermost mantle become too dense to float on the underlying asthenosphere, so it subducts into the mantle. The subducted oceanic lithosphere ultimately mixes with the asthenosphere and mesosphere.
4. Each type of plate boundary is associated with various features and activities. In the table below check-off which apply:
|
FEATURE/ACTIVITY |
DIVERGENT |
TRANSFORM |
C O N V E R G E N T |
||
|
OCEAN-OCEAN |
OCEAN-CONTINENT |
CONTINENT-CONTINENT |
|||
|
Oceanic ridge |
X |
* |
|
|
|
|
Rift valley |
X |
|
|
|
|
|
Basaltic volcanism |
X |
|
|
|
|
|
Andesitic volcanism |
|
|
X |
X |
|
|
Deep sea trench |
|
|
X |
X |
|
|
Island arc |
|
|
X |
|
|
|
Volcanic arc |
|
|
|
X |
|
|
Accretionary prism |
|
|
X |
X |
|
|
Forearc basin |
|
|
X |
X |
|
|
Foreland fold and thrust belt |
|
|
|
X |
|
|
Foreland basin |
|
|
|
X |
|
|
Normal faults |
X |
|
|
|
|
|
Reverse faults |
|
|
X |
X |
X |
|
Strike-slip faults |
|
X |
|
|
|
|
Shallow earthquakes |
X |
X |
X |
X |
X |
|
Deep earthquakes |
|
|
X |
X |
|
|
Benioff zone |
|
|
X |
X |
|
|
Subduction zone |
|
|
X |
X |
|
|
Fracture zone |
|
** |
|
|
|
|
Suture zone |
|
|
|
|
X |
*Transform plate boundaries usually form between offset ridge segments.
**Fracture zones are not plate boundaries. They extend outward from the transform plate boundaries that occur between offset ridge segments and represent seafloor age and depth discontinuities.
5. California is made of continental crust which is too buoyant (relative to the mantle) to sink much below sea level.
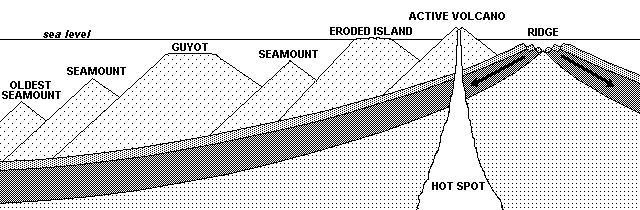
6. Draw a diagram that illustrates how hot spots produce island/seamount/guyot chains.
8800 Grossmont College Drive
El Cajon, California 92020
619-644-7000
Accessibility
Social Media Accounts